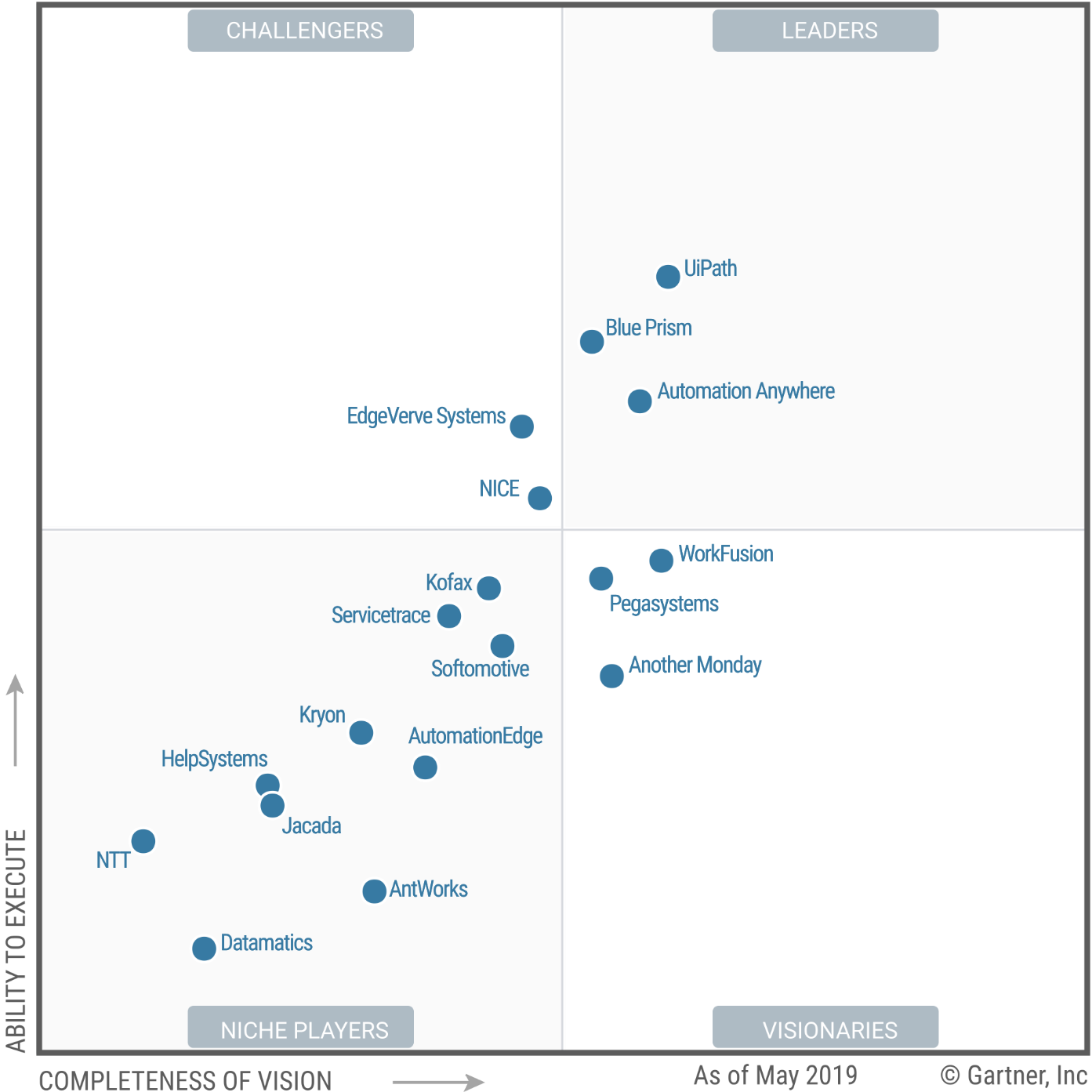
Ukazał się Raport Gartnera na temat robotów software’owych RPA. Gratulujemy UiPath, partnerowi programu Digital Finance Excellence zaszczytnego i korzystnego miejsca lidera!!!
Poniżej krótki fragment. Polecamy lekturę całego raportu dostępnego na www.gartner.com
„RPA tools enable the enterprise to use a full range of developer personas ? citizen developers (most commonly business analysts, as well as business end users); departmental developers; and enterprise IT professionals ? and to develop integrations that range from tactical to strategic. Three RPA use cases follow.
Use Case No. 1: Integration Using an Application?s UI
Organizations have a plethora of existing systems. Citizen developers and business analysts can quickly extract related data from System 1 and make it available in System 2:
-
Data transfer and/or matching between systems. Systems can be legacy systems, enterprise applications or personal productivity tools (e.g., Excel).
-
Integration where no back-end integration or API is available ? i.e., it is only possible via the application?s UI.
-
May also apply to scenarios in which automation is later embedded in third-party applications.
Use Case No. 2: Large-Scale Data Migration
An automation extracts data automatically from several systems, using carefully structured scripts to access existing systems and other data sources for a new target system. This involves:
-
System migration and (re)configuration involving multiple data sources.
-
New systems development involving third-party applications and long-running processes.
-
Pruning data from applications to ensure that only the relevant information is used (e.g., only relevant emails, relevant cases, relevant news from news or other evolving websites).
Use Case No. 3: Augment Knowledge Workers
Automations extract information from related documents and systems, shaping it and preparing it for consumption by knowledge workers at the point of need. While interacting with a customer or external stakeholder, data and information from many systems might be required. A knowledge worker typically accesses multiple systems to assemble this material. That worker may also need to interact with many colleagues, each of whom have systems to deal with, which can take a long time and affect the customer?s experience significantly. This involves:
-
Prechecking and structuring data for easy consumption.
-
Provision of contextual information to support the customer case, which may include advice on the best next action, or related scenarios.
-
Delivering output to relevant applications depending on the data, or steering actions on a website/chatbot.
-
Ultimately, this could lead to a situation in which a chatbot is interacting with the customer directly, only handing off to a human knowledge worker when things occur outside its ability to handle directly.
As these different usage scenarios become more complicated, they may need more of the tangential capabilities that are outside of our core definition of the RPA market. These include NLP, machine learning, longer-running processes and OCR integrations/features.”